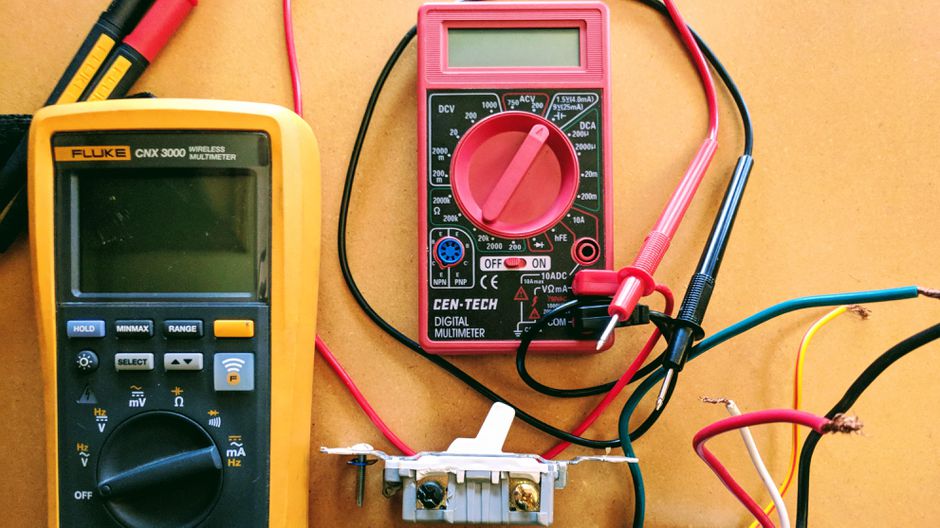
What is a multimeter?
A multimeter is an electronic tool used to measure voltage, amps, and resistance across circuits.
By attaching two leads to different parts of an electrical system, a
multimeter can be used to detect levels of voltage and resistance or changes
in electrical currents.
The first multimeter was introduced in the late 1970s and has proven much more accurate and reliable than the old needle-based analog meters. It’s used primarily to measure voltage (volts), current (amps), and resistance (ohms).
Uses of a multimeter
A multimeter can be a hand-held device useful for basic fault finding and field service work or a
bench instrument that can measure to a very high degree of accuracy. They can
be used to troubleshoot electrical problems in a wide array of industrial and
household devices such as electronic equipment, motor controls, domestic
appliances, power supplies, and wiring systems.
Types of multimeters
Multimeters are divided into two types depending on the way the indication is displayed: Analog and Digital
Analog multimeters are multifunction electrical measuring instruments with indication by means of an analog scale.
Digital multimeters are modern, reliable measuring devices characterized by
high measurement accuracy and various functional capabilities. Digital
multimeters have replaced analog in connection with the possibility of wide
application of semiconductor technologies.
Take a moment to see some of the best and durable multi-meters:
Some multimeters have continuity check, resulting in a aloud beep if two things are electrically connected. This is helpful if, for instance, you are building a circuit and connecting wires or soldering; the beep indicates everything is connected and nothing has come loose. You can also use it to make sure two things are not connected, to help prevent short circuits.
Some multimeters also have a diode check function. A diode is like a one-way valve that only lets electricity flow in one direction. The exact function of the diode check can vary from multimeter to multimeter. If you are working on a diode and can't tell which way it goes in the circuit, or if you are not sure the diode is working properly, the check feature can be quite handy.
Advanced multimeters might have other functions, such as the ability to measure and identify other electrical components, like transistors or capacitors.
Types of Multimeter Applications
The applications of types of multimeter mainly involve various electrical and electronic projects for components testing and also used in different measurement applications in the multimeter.
Temperature and Environmental Application
- Low-cost weather station
- DMM internal temperature
Votage measurements
- High and low-value DC measurements
- Peak to Peack and DC average measurements
Current measurements
- DC measurements
- True RMS AC
Resistance measurements
- Micro ohmmeter
- Measuring resistance with constant voltage
- Measuring resistance with constant current
Time and frequency measurement
- Fast frequency
- Time measurement
Multimeters are absolutely
necessary for any type of electrical work. From installing a ceiling fan to
changing a junction box, using a multimeter helps
determine if wires are hot or not and so many more. Click here to source for
the best multimeters on www.stockcheck.com
 Share
Share